Climbing the Ladder: Big 4 Accountant Salary Growth
Welcome to the exciting world of being a Big 4 accountant! You’ve worked hard to get to where you are, and now it’s time to see just how far your salary can climb in the first five years of your career. Buckle up, because the journey ahead is going to be a thrilling one!
In your first year as a Big 4 accountant, you can expect to earn a competitive salary that reflects your hard work and dedication. The starting salary for entry-level accountants at the Big 4 firms is typically in the range of $50,000 to $60,000 per year. This may vary depending on the location of your office and your level of experience, but rest assured that you’ll be well compensated for your efforts.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bigfour-0e7f1f82c9294d788286e4a66b7f06ee.jpg)
Image Source: investopedia.com
As you move into your second year at the Big 4, you can expect to see a significant increase in your salary. With a year of experience under your belt, you’ll likely be eligible for a raise that bumps your salary up to the $60,000 to $70,000 range. This increase reflects the valuable skills and knowledge you’ve gained in your first year on the job, and sets the stage for even more growth in the years to come.
By the time you reach your third year as a Big 4 accountant, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a seasoned professional. At this point, you can expect to see another bump in your salary, with earnings in the range of $70,000 to $80,000 per year. This increase reflects your continued growth and development as an accountant, and positions you for even greater opportunities in the future.
In your fourth year at the Big 4, you’ll likely be hitting your stride as a fully-fledged accountant. With four years of experience under your belt, you can expect to earn a salary in the range of $80,000 to $90,000 per year. This significant increase reflects the hard work and dedication you’ve put into your career, and sets you up for continued success in the years ahead.

Image Source: big4accountingfirms.com
And finally, in your fifth year as a Big 4 accountant, you’ll be at the top of your game. With five years of experience and a wealth of knowledge behind you, you can expect to earn a salary in the range of $90,000 to $100,000 per year. This represents a significant milestone in your career, and positions you as a leader in your field with even greater earning potential in the years to come.
So there you have it – the salary progression of a Big 4 accountant in the first five years of their career. From your humble beginnings as an entry-level accountant to your triumphant rise to the top of the pay scale, the journey ahead is sure to be an exciting one. So buckle up, keep working hard, and get ready to climb the ladder to success as a Big 4 accountant!
Navigating the Pay Scale: Your First 5 Years in the Big 4
So, you’ve landed a job at one of the prestigious Big 4 accounting firms – congratulations! You’ve worked hard to get to this point, and now it’s time to reap the rewards. But what exactly can you expect in terms of salary progression in your first five years at a Big 4 firm? Let’s take a closer look at what lies ahead as you navigate the pay scale in the world of Big 4 accounting.
![image.title Top Accounting Firms in the US [Updated ] image.title Top Accounting Firms in the US [Updated ]](https://big4accountingfirms.org/wp-content/uploads/Black-Numbered-List-Animated-Your-Story-1.jpg)
Image Source: big4accountingfirms.org
Year 1: The Starting Point
In your first year as a Big 4 accountant, you can expect to earn a competitive salary that reflects your entry-level position. While the exact figure may vary depending on the firm and your location, you can generally expect to earn a solid starting salary that is higher than the industry average for entry-level accountants. This is a great starting point as you begin your career in the world of Big 4 accounting.
Year 2: Moving Up the Ranks

Image Source: big4bound.com
As you gain more experience and expertise in your role, you can expect to see a significant increase in your salary in your second year at a Big 4 firm. This pay rise is often a reflection of the value you bring to the firm and the increased responsibilities you take on as you move up the ranks. You may also have the opportunity to receive bonuses or other incentives based on your performance, further boosting your overall compensation.
Year 3: Establishing Yourself
By your third year at a Big 4 firm, you should have established yourself as a competent and reliable member of the team. This can lead to further salary increases and potentially even more opportunities for advancement within the firm. You may also have the chance to take on new challenges and responsibilities that can help you continue to grow and develop in your role as a Big 4 accountant.
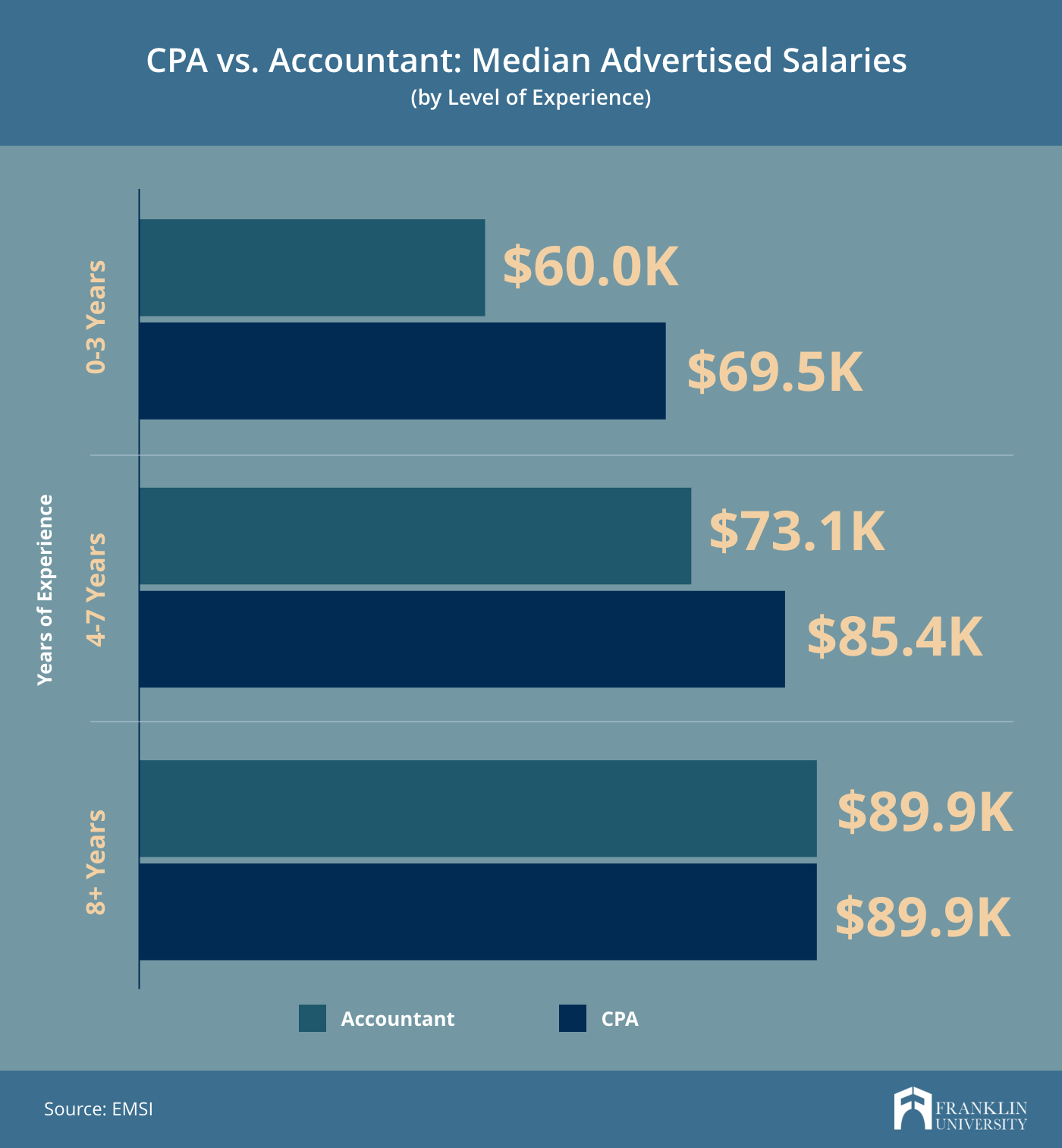
Image Source: franklin.edu
Year 4: Reaping the Rewards
In your fourth year at a Big 4 firm, you can expect to see even more rewards for your hard work and dedication. This may come in the form of salary increases, bonuses, or other incentives that reflect your continued growth and success within the firm. By this point, you should have a solid understanding of the firm’s expectations and be well on your way to establishing yourself as a valued member of the team.
Year 5: The Sky’s the Limit

Image Source: cloudfront.net
By your fifth year at a Big 4 firm, the sky’s the limit in terms of your salary progression. With five years of experience under your belt, you should be well-positioned to take on more senior roles within the firm and command a salary that reflects your expertise and leadership abilities. This can open up even more opportunities for career advancement and growth as you continue to climb the ladder in the world of Big 4 accounting.
In conclusion, the salary progression of Big 4 accountants in their first five years is a reflection of their hard work, dedication, and expertise in the field. By navigating the pay scale with confidence and determination, you can expect to see steady growth in your salary and overall compensation as you continue to advance in your career. So, buckle up and get ready for an exciting journey ahead as you navigate the pay scale in the world of Big 4 accounting!
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash-accounting-history-FINAL2-ed732e3d3f4e443288fbcc9a601fc23b.jpg)
Image Source: investopedia.com
What Big 4 Accountants Earn in Their First 5 Years
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bigfour-0e7f1f82c9294d788286e4a66b7f06ee.jpg?w=940&resize=940,0&ssl=1)


