Finding Your Financial Fairy Godmother
When it comes to managing your finances, it can often feel like you’re lost in a maze with no clear path to success. That’s where a financial advisor comes in – they’re like your own personal fairy godmother, guiding you through the financial world and helping you make smart decisions that will set you up for a secure future.
But how do you find the perfect financial fairy godmother for you? Here are a few tips to help you on your quest:

Image Source: kc-usercontent.com
1. Define Your Goals: Before you start your search for a financial advisor, take some time to define your financial goals. Do you want to save for retirement, buy a home, or start a business? Having a clear understanding of what you want to achieve will help you find an advisor who specializes in helping clients like you reach their goals.
2. Do Your Research: Once you know what you’re looking for in a financial advisor, it’s time to start your search. Look for advisors who have experience working with clients in similar situations to yours and who have a track record of success. Read reviews, ask for recommendations from friends and family, and don’t be afraid to schedule initial consultations with multiple advisors to find the best fit.
3. Ask the Right Questions: During your initial consultations with potential advisors, don’t be afraid to ask tough questions. Find out about their experience, qualifications, and approach to financial planning. Make sure they have a clear fee structure and that you understand how they will be compensated for their services. It’s important to find an advisor who is transparent and who you feel comfortable working with.

Image Source: cql-aws.com
4. Trust Your Gut: Finding the right financial advisor is about more than just qualifications and experience – it’s also about finding someone you trust and feel comfortable with. Pay attention to how you feel during your consultations with potential advisors. Do you feel heard and understood? Do you feel like they have your best interests at heart? Trust your instincts and choose an advisor who feels like the right fit for you.
5. Build a Relationship: Once you’ve found your financial fairy godmother, it’s important to nurture your relationship. Keep the lines of communication open, be honest about your financial goals and concerns, and make sure to check in regularly to review your progress. A good financial advisor will be there to support you every step of the way and help you navigate any financial challenges that come your way.
Finding the right financial advisor can be a game-changer when it comes to managing your finances and planning for the future. By following these tips and trusting your instincts, you can find your perfect match and set yourself up for financial success. So go ahead, wave your magic wand and find your financial fairy godmother today!
Unlocking the Secret to Financial Advisor Harmony

Image Source: maryville.edu
When it comes to managing your finances, finding the right financial advisor can make all the difference. Just like finding the perfect partner, it is important to find someone who understands your goals, values, and needs. But how do you unlock the secret to financial advisor harmony?
The first step is to do your research. Take the time to explore different financial advisors and their areas of expertise. Look for someone who specializes in the areas that are most important to you, whether that be retirement planning, investment strategies, or tax planning. It is also important to consider their qualifications and experience. A certified financial planner (CFP) or chartered financial analyst (CFA) designation can give you peace of mind knowing that your advisor has the necessary knowledge and skills to help you reach your financial goals.
Next, consider your personal compatibility with the financial advisor. Just like any relationship, communication is key. Make sure that you feel comfortable talking to your advisor and that they listen to your concerns and goals. Trust is also crucial in a financial advisor-client relationship, so make sure that you feel confident in their abilities and judgement.
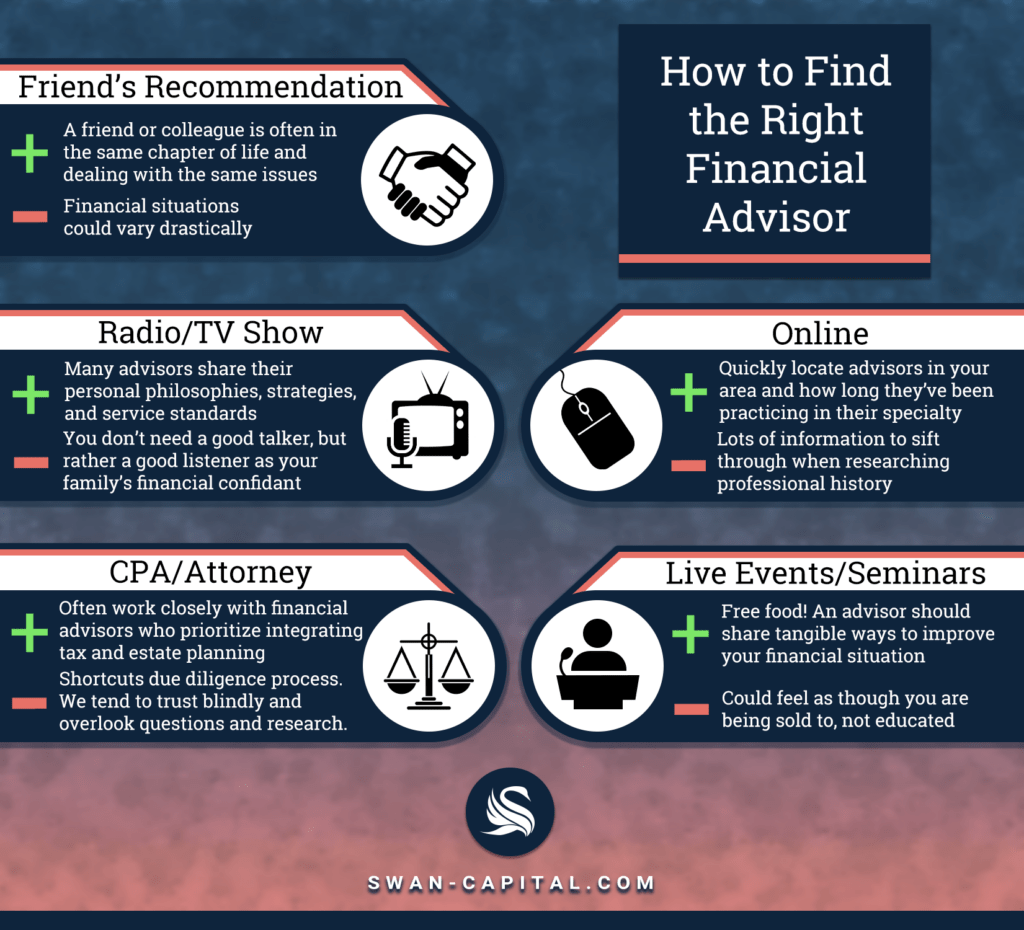
Image Source: swan-capital.com
Another important factor to consider is the fee structure of the financial advisor. Some advisors charge a flat fee, while others work on a commission basis. It is important to understand how your advisor is compensated and to make sure that their fee structure aligns with your financial goals. Transparency is key when it comes to fees, so make sure that you are clear on what you will be paying for the services provided.
In addition to finding a financial advisor who meets your technical and personal needs, it is also important to consider their investment philosophy. Some advisors may be more conservative in their approach, while others may be more aggressive. Make sure that your advisor’s investment philosophy aligns with your risk tolerance and financial goals.
Once you have found a financial advisor who meets all of your criteria, the next step is to establish a plan and set goals. Your advisor should work with you to develop a comprehensive financial plan that takes into account your current financial situation and long-term goals. Regular check-ins and updates are important to ensure that you are on track to meeting your goals and to make any necessary adjustments along the way.

Image Source: website-files.com
In conclusion, finding the right financial advisor is essential to achieving financial success. By doing your research, establishing a strong personal connection, understanding the fee structure, and aligning investment philosophies, you can unlock the secret to financial advisor harmony. Remember, your financial advisor is there to help guide you on your financial journey, so make sure that you find someone who is the perfect match for your needs and goals.
How to Choose a Financial Advisor or Planner

Image Source: christineluken.com



