Saving vs Investing: Prioritizing Your Financial Goals
Building a Bright Future: Saving vs Investing
When it comes to managing your finances, one of the key decisions you’ll need to make is whether to focus on saving or investing. Both saving and investing are important aspects of financial planning, but they serve different purposes and can help you achieve different goals. Understanding the difference between the two and knowing when to prioritize one over the other can help you build a bright financial future for yourself.
Saving is the act of setting aside a portion of your income for future use. This could be for short-term goals, such as building an emergency fund or saving for a vacation, or for long-term goals, such as buying a home or retiring comfortably. Saving is important because it provides you with a financial safety net and helps you avoid going into debt when unexpected expenses arise.
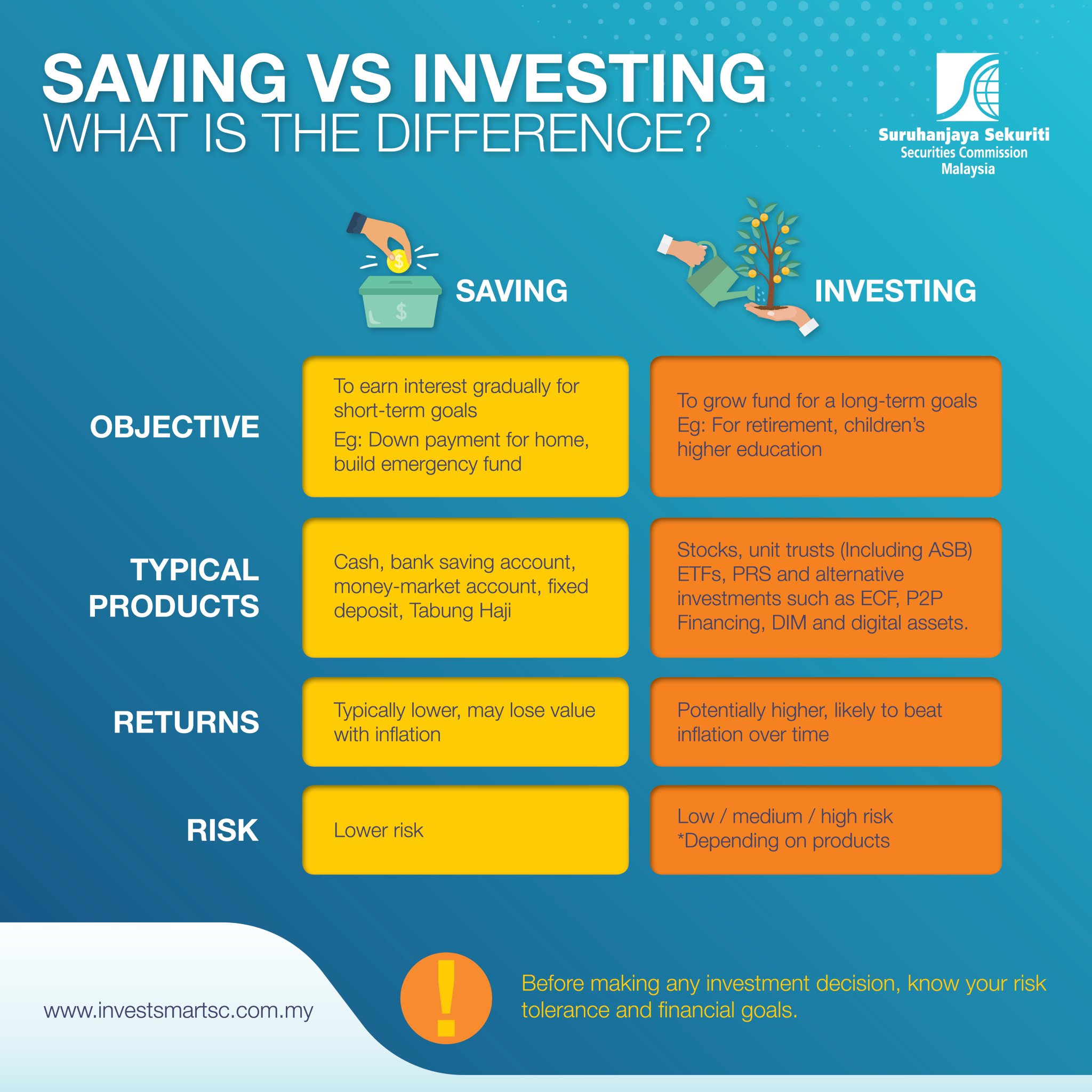
Image Source: twimg.com
Investing, on the other hand, involves putting your money into assets with the expectation of generating a return. This could include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate, or other types of investments. Investing is a way to make your money work harder for you and can help you build wealth over time. While investing comes with more risk than saving, it also has the potential for higher returns.
When it comes to prioritizing your financial goals, it’s important to strike a balance between saving and investing. Saving should always come first, as having an emergency fund and cash reserves can help protect you from financial shocks and give you peace of mind. Experts recommend saving at least three to six months’ worth of living expenses in an easily accessible account before considering investing.
Once you have a solid savings foundation in place, you can start thinking about investing for the future. Investing can help you achieve long-term financial goals, such as buying a home, sending your children to college, or retiring comfortably. By putting your money to work in the market, you can take advantage of compounding returns and potentially grow your wealth over time.

Image Source: squarespace-cdn.com
One way to prioritize your financial goals is to create a savings plan that includes both short-term and long-term objectives. Start by setting specific savings targets for things like emergencies, vacations, major purchases, and retirement. Once you have a clear idea of what you’re saving for, you can allocate your money accordingly and decide how much to put towards investing.
Another important factor to consider when prioritizing your financial goals is your risk tolerance. Saving is generally considered low risk, as the money you put aside is typically kept in a secure account like a savings or money market account. Investing, on the other hand, comes with more risk, as the value of your investments can fluctuate with the market. Before deciding to invest, it’s important to assess your risk tolerance and make sure you’re comfortable with the potential ups and downs of the market.
In conclusion, saving and investing are both important components of financial planning, and each serves a different purpose in helping you achieve your financial goals. By prioritizing saving for emergencies and building a solid financial foundation, you can set yourself up for future success and reduce your reliance on debt. Once you have a savings plan in place, you can start thinking about investing for the future and growing your wealth over time. Remember to strike a balance between saving and investing, consider your risk tolerance, and stay focused on your financial goals to build a bright financial future for yourself.
Making Your Money Work Harder: Financial Goals
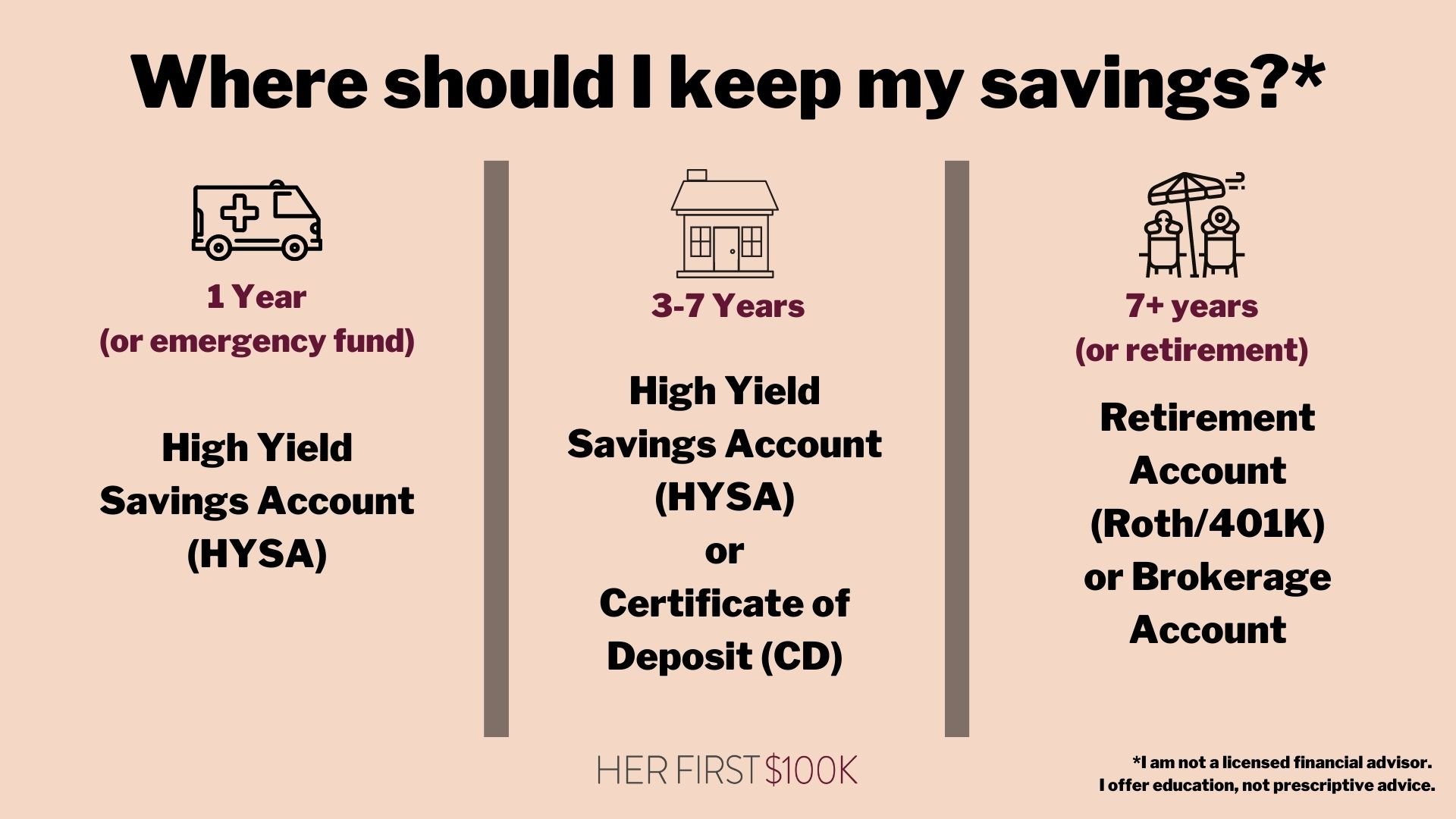
Image Source: herfirst100k.com
When it comes to managing your finances, one of the key decisions you’ll have to make is how to prioritize your financial goals. Should you focus on saving money for the future, or should you invest your money in order to potentially earn a higher return? The answer to this question will depend on a variety of factors, including your current financial situation, your long-term financial goals, and your risk tolerance. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of setting financial goals and the benefits of both saving and investing in order to achieve those goals.
Setting financial goals is essential for anyone who wants to achieve financial success. Without clear goals in mind, it’s easy to lose track of your spending and saving habits, and you may find yourself struggling to make progress towards your long-term objectives. By setting specific, measurable financial goals, you can create a roadmap for your financial future and stay motivated to make the necessary changes to reach those goals.
When it comes to prioritizing your financial goals, it’s important to consider both short-term and long-term objectives. Short-term goals may include building an emergency fund, paying off high-interest debt, or saving for a major purchase like a new car or a vacation. Long-term goals, on the other hand, may include saving for retirement, buying a home, or funding your children’s education. By prioritizing your goals and creating a plan to achieve them, you can ensure that you’re making the most of your financial resources.

Image Source: nationwide.com
Saving money is an important part of achieving your financial goals, as it provides you with a safety net for unexpected expenses and helps you build wealth over time. By saving a portion of your income each month, you can gradually accumulate a nest egg that can be used to achieve your long-term goals. Whether you’re saving for retirement, a down payment on a house, or a dream vacation, having a dedicated savings plan in place can help you stay on track and avoid the temptation to spend money on impulse purchases.
Investing, on the other hand, offers the potential for higher returns on your money, but it also comes with greater risk. When you invest your money in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or other assets, you have the opportunity to earn a higher rate of return than you would by keeping your money in a savings account. However, investing also carries the risk of losing money if the value of your investments declines. For this reason, it’s important to carefully consider your risk tolerance and investment timeline before deciding how to allocate your financial resources.
One common strategy for prioritizing your financial goals is to focus on saving for short-term goals while also investing for long-term objectives. By setting aside a portion of your income for both saving and investing, you can build a solid financial foundation while also working towards building wealth over time. This balanced approach allows you to have the security of a savings cushion while also taking advantage of the potential growth opportunities offered by investing in the stock market or other asset classes.

Image Source: website-files.com
In conclusion, prioritizing your financial goals is a key step towards achieving financial success. By setting clear, measurable goals and creating a plan to achieve them, you can make the most of your financial resources and work towards building a secure financial future. Whether you choose to focus on saving, investing, or a combination of both, the important thing is to take control of your finances and make your money work harder for you. By setting financial goals and working towards them consistently, you can take charge of your financial future and turn your dreams into reality.
Saving vs Investing: Which Comes First?

Image Source: licdn.com



